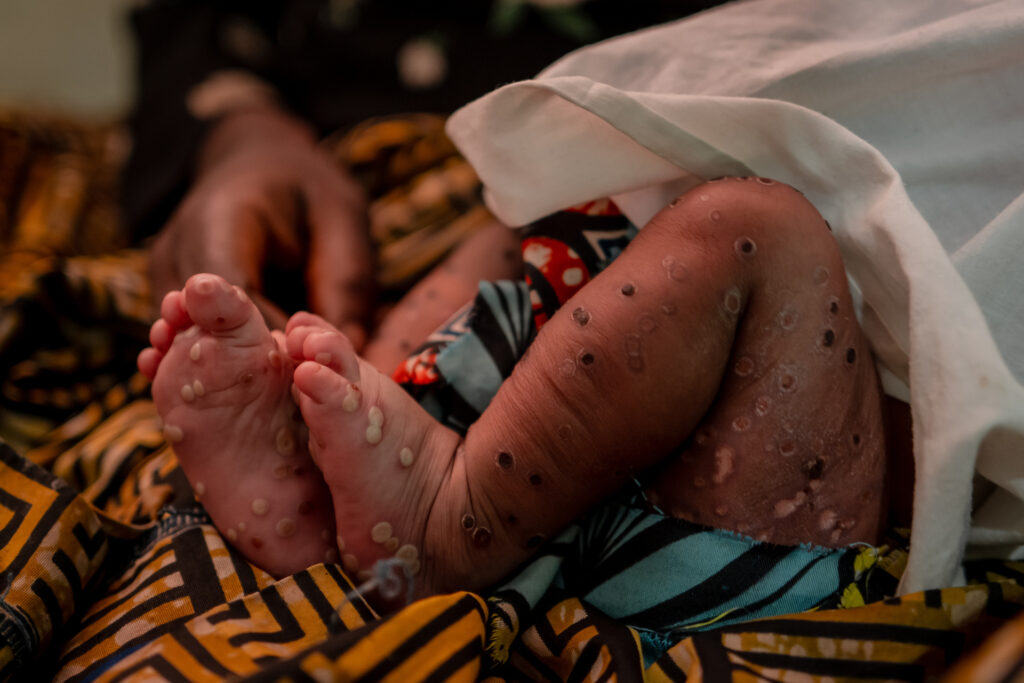
The emergence of mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) has captured global attention since its sudden outbreak in May 2022. Having originated in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the disease underwent a rapid expansion, permeating societies across six WHO regions. This article takes a closer look at the global spread and impact of mpox, elucidating how its influence has varied by region.
Global Spread of Monkeypox
When mpox made headlines in 2022, few anticipated its swift infiltration into societies worldwide. The outbreak precipitated a wave of infections that primarily affected men who have sex with men, a demographic that found itself at the center of this public health crisis. The mode of transmission became a focal point, as person-to-person spread predominantly occurred through intimate networks.
Key points regarding the global spread include:
- Timeline : The outbreak began in May 2022 and has continued to escalate, leading to over 120 countries reporting cases by mid-2024.
- Laboratory-Confirmed Cases : More than 100,000 laboratory-confirmed cases have been documented during this period, indicating a severe public health challenge.
- Death Toll : Tragically, over 220 confirmed deaths have been attributed to mpox, primarily affecting populations in certain vulnerable regions.
The rapid proliferation of mpox can be attributed to a lack of awareness and understanding of the disease, particularly in newfound regions. Communities worldwide were unprepared for the waves of misinformation and stigma accompanying the outbreak, which further complicated effective public health responses.
Impact on Different Regions
As mpox carved its path across the globe, it did not affect all regions equally. The impact varied widely, influenced by existing health infrastructures, social practices, and the level of community engagement in public health campaigns.
- Europe and the Americas : In these regions, the initial cases were notable within certain social networks. This fact not only emphasized the importance of targeted health interventions but also highlighted the urgent need to combat stigma. It is crucial to remember that public health efforts are often undermined when affected individuals hesitate to seek care due to societal prejudice.
- Africa : The Democratic Republic of the Congo, where mpox has historically been endemic, has witnessed an alarming increase in cases and fatalities. Limited healthcare resources, compounded by political instability, have rendered communities highly vulnerable. Refugee camps in the Republic of the Sudan also faced outbreaks, showcasing how conflict can exacerbate health crises.
- Asia and the Middle East : Although not initially hit as hard, these regions began reporting cases as the outbreak spread. Health authorities were prompted to act swiftly in the face of emerging clusters, underscoring the need for robust surveillance systems.
Despite the grim statistics, it’s crucial to note the resilience of communities. In many areas, individuals rallied to support those affected, providing care and fostering awareness. For example, local NGOs organized educational campaigns aimed at dispelling myths surrounding mpox, creating safe spaces for dialogue, and offering medical resources.
Communities also demonstrated ingenuity by utilizing social media platforms to spread crucial information, emphasizing shared responsibilities in combating the disease. This grassroots involvement became instrumental in efforts to contain further spread.
In conclusion, the spread of mpox across various global landscapes has served as a mirror reflecting the disparities in health responses. Together, the experiences from different regions underscore the importance of early intervention, robust health systems, and, above all, compassionate communities that prioritize health over stigma. As the world continues to navigate the mpox outbreak, a collective response that incorporates lessons learned from each region will be essential for combating future health crises effectively.
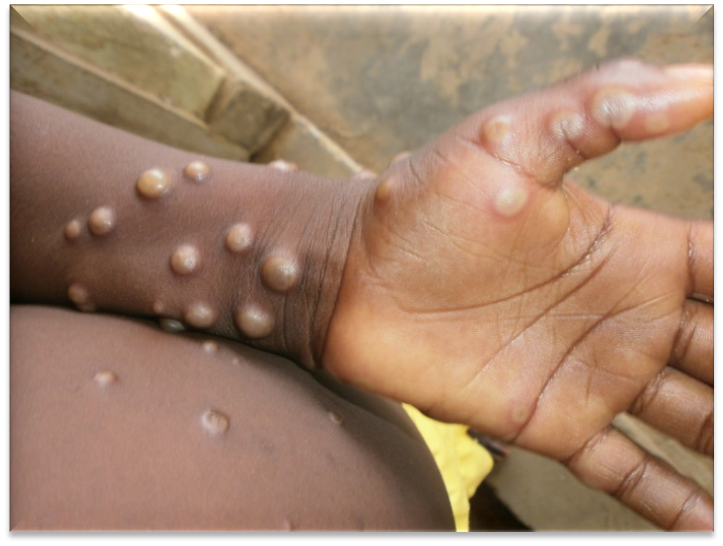
Outbreaks and Variants
As the global health community has grappled with the ongoing mpox crisis, understanding the outbreaks and the emergence of different variants has become crucial for effective management and prevention. Since the first reports of infection in May 2022, the dynamics of the disease have evolved, showcasing new challenges amidst ongoing public health responses.
Clade I Outbreaks in 2022
The initial outbreaks of mpox identified in 2022 were predominantly associated with what scientists refer to as Clade I. This clade’s rapid spread raised alarms worldwide, particularly because of its unique epidemiological patterns.
- Origins and Spread : The entry of Clade I into various global regions was marked by significant outbreaks in Europe and the Americas. During the early days of the outbreak, it became clear that the virus was primarily transmitting through sexual networks. It quickly became evident that this would require targeted public health strategies focused on affected demographics.
- Impact in Vulnerable Locations : An alarming feature of Clade I’s spread was its presence in refugee camps, particularly in the Republic of the Sudan. Close quarters, coupled with limited access to healthcare, amplified the risk of transmission in these environments. The rapid availability of information was vital for prevention efforts, with health agencies urging individuals to come forward for testing and support.
- Response from Communities : Several grassroots organizations emerged to mitigate the outbreak’s impact. Local healthcare workers and volunteers created informational campaigns to educate at-risk populations and destigmatize the disease. One notable initiative involved distributing materials in community centers and social hubs, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice and vaccinations.
With several months of data accumulating, public health officials began examining ways to counter the spread effectively. A combination of education, vaccination campaigns, and community engagement proved essential, providing a foundation for managing the outbreak.
Emergence of Clade Ib
As the situation evolved, so did the virus itself. By mid-2024, healthcare professionals began identifying clade Ib, a new offshoot of Clade I. This development raised several red flags among public health officials and amplified the importance of continued vigilance.
- Characteristics of Clade Ib : Clade Ib is distinct in its transmission patterns, with evidence suggesting it is spreading through person-to-person contact within communities. This was a significant shift from the earlier characteristics of Clade I, underscoring the need for adaptive public health responses.
- Spread Beyond Origins : The emergence of Clade Ib gave rise to concerns about its potential spread to other countries outside the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it was first recognized. By scrutinizing patterns of transmission, public health entities could proactively prepare for potential outbreaks.
- Communication and Awareness Efforts : As clade Ib began to surface, targeted awareness campaigns were reinstated to educate communities on recognizing symptoms early. The role of health communication cannot be understated during these times; ensuring that affected populations felt supported and informed could significantly influence the outcomes of containment strategies. Health workers stressed the importance of regular check-ups and symptom awareness to encourage a community-focused response.
The dynamic nature of mpox outbreaks, especially with the emergence of new variants like clade Ib, underscores the need for robust healthcare systems and a community-centered approach to disease prevention. By adapting to these challenges, public health entities can better prepare for the future.
In conclusion, the ongoing study of mpox variants exemplifies the importance of remaining agile in public health strategies. The lessons learned from the Clade I outbreaks and the emergence of Clade Ib can guide future efforts, ensuring that communities are better equipped to face evolving health threats. The key lies in collaboration, education, and a strong commitment to combating the stigma that often hinders public health efforts.
Case Statistics
The narrative surrounding mpox is supported largely by the data it generates, providing insight into the outbreak’s scope and severity. Understanding the statistics around laboratory-confirmed cases and reported deaths is crucial as these figures not only frame the public health response but also reflect the challenges faced by communities worldwide.
Laboratory-Confirmed Cases Worldwide
As we analyze the case statistics, it’s important to recognize the staggering numbers that characterize the mpox outbreak. Between January 2022 and August 2024, more than 120 countries reported laboratory-confirmed cases of mpox.
- Total Cases : Over 100,000 laboratory-confirmed cases have been documented globally. This figure is notably high for a disease that was not widely known outside certain regions until the recent outbreaks.
- Geographical Distribution : The spread of cases is not uniform. Countries in Europe and the Americas accounted for a significant percentage of infections, highlighting the virus’s ability to rapidly adapt and navigate social networks.
- Demographics : Initial reports indicated that mpox affected primarily gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men. However, the reach of the virus extended beyond these demographics, affecting individuals from various backgrounds, ages, and sexual orientations. This shift underlines the necessity for public health campaigns that address all communities rather than just targeted groups.
Examples from the field illustrate the impact of rising case numbers. In 2022, frontline healthcare workers in the United States faced overwhelming demand for vaccinations and testing, leading to situations where supply struggled to meet the surge in demand. Community health centers became overburdened, emphasizing the importance of strong healthcare systems during outbreaks.
Reported Deaths Due to Monkeypox
While the number of confirmed cases is alarming, the mortality rate associated with mpox is equally concerning. With over 220 reported deaths among confirmed cases, the human toll of this outbreak is significant.
- Mortality Rate : Although the overall mortality rate for mpox remains relatively low compared to other contagious diseases like Ebola, it is still a cause for concern. The death rate can vary based on factors such as geographic region, existing healthcare infrastructure, and the presence of underlying health conditions among affected populations.
- Impact on Vulnerable Populations : The most severe effects have been felt in regions with strained healthcare systems, such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where health resources are limited. Here, the combination of mpox infections and other endemic diseases poses a greater risk to vulnerable populations.
- Personal Stories : For communities impacted, the statistics translate into personal losses and heartbreak. Many have shared stories of loved ones falling ill and the ripple effect it creates within families and local communities. In discussing mpox, it’s essential to acknowledge the human stories behind the numbers. These narratives resonate deeply, emphasizing the urgent need for effective public health strategies to reduce transmission.
In sum, the statistics surrounding mpox cases and deaths serve as a reflection of both the successes and challenges of the response to this outbreak. They illustrate the inequities faced by different regions and demographics, underscoring the importance of a tailored approach that considers local contexts. Through ongoing public health efforts, the hope remains that communities can turn the tide on this disease, reducing both the number of cases and fatalities moving forward.
As we continue to monitor the situation, these figures call for heightened awareness and action across all levels of society. By recognizing the data and its implications, we forge a path to understanding and addressing the complexities of mpox, striving for a healthier future for everyone.
WHO Response
In the face of the mpox outbreak, the World Health Organization (WHO) has taken significant steps to mitigate the impact of the disease while emphasizing the importance of collaboration and resource sharing among member states. This response has involved various prevention and intervention measures, highlighting the organization’s commitment to global health and safety.
Prevention and Response Efforts
From the initial identification of mpox in May 2022, WHO activated a multi-faceted approach to control the burgeoning outbreak, driven by the urgency to protect communities worldwide. Let’s delve into some of the major initiatives undertaken:
- Surveillance and Monitoring : WHO established enhanced monitoring systems to track mpox cases across regions effectively. This has involved collaboration with local health authorities to ensure timely reporting and identification of new cases. Surveillance is instrumental in understanding the transmission dynamics and tailoring public health responses.
- Guidelines and Recommendations : Clear guidelines were developed for healthcare providers and the general public. WHO emphasized the importance of awareness campaigns that inform people about the virus, its symptoms, and preventive measures. For instance, educational materials were distributed in at-risk communities, particularly targeting information dissemination among LGBTQ+ populations, which have been disproportionately affected.
- Vaccination Initiatives : Vaccines play a pivotal role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases. WHO has coordinated efforts to distribute vaccines, especially to frontline workers and at-risk populations. The organization worked tirelessly to facilitate equitable access to vaccines, ensuring that all member states, particularly those with fewer resources, received the tools needed to combat mpox.
- Partnerships and Stakeholder Engagement : WHO recognized the importance of partnerships with various stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and community organizations. These collaborations were designed not only to address healthcare needs but also to tackle stigma and discrimination associated with mpox. People often hesitate to seek medical care due to fear of societal judgment, and WHO’s efforts included promoting acceptance and support within communities.
- Research Coordination : Understanding the virus requires continuous research and innovation. WHO has helped coordinate research into effective treatments and vaccines, providing a platform for sharing findings and engaging with researchers across the globe. This approach maximizes the impact of research efforts and ensures that findings benefit public health initiatives efficiently.
Declarations of Public Health Emergency
Amid escalating concerns about mpox, WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus declared mpox a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) twice—first in May 2022 and again in August 2024. This declaration underscores the seriousness of the situation and mobilizes international resources to respond appropriately.
- Implications of the PHEIC Declaration : When a PHEIC is declared, it serves as a signal for countries to intensify their response efforts, including enhancing surveillance, strengthening healthcare systems, and mobilizing funding for disease control measures. Countries that may have faced challenges in addressing the outbreak are provided with additional support and resources.
- Focus on Global Unity : The declaration also calls for global unity in combating the outbreak. Countries are encouraged to adopt consistent strategies in managing mpox, share data transparently, and collaborate on vaccine distribution. This sense of solidarity emphasizes the interconnectedness of public health—no country is an island in the face of epidemics.
- Community-Centric Approach : WHO’s declarations have also prompted discussions around integrating community feedback into health initiatives. Communities affected by mpox are vital partners in crafting responsive public health measures that address their unique needs and experiences.
In conclusion, the WHO’s response to the mpox outbreak reflects an adaptive strategy focused on collaboration, education, and resource sharing. By declaring mpox a PHEIC, WHO has emphasized the urgent need for collective action to combat this disease. As the world continues to navigate this evolving health crisis, the work of WHO and its partners remains instrumental in fostering a safer, healthier global community. Together, through coordinated efforts, there is hope for reducing the impact of mpox and curtailing its future spread.
Research and Vaccine Development
As the mpox outbreak continues to reshape public health narratives across the globe, research and vaccine development have emerged as pivotal components in the fight against this infectious disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) has rallied resources and expertise to prioritize substantial research coordination and promote equitable access to these essential tools. Let’s delve into both these aspects as they play a crucial role in managing this evolving health crisis.
Coordination of Research
Effective research coordination is vital in a fast-paced public health emergency like the mpox outbreak. WHO has excelled in bringing together diverse stakeholders, including governments, researchers, and academic institutions, to facilitate rapid advancements in understanding the virus and developing effective countermeasures.
- Global Research Networks : WHO has helped establish global research networks that enable researchers to share information, findings, and best practices. Through regular meetings and online forums, scientists and public health officials can discuss emerging data and streamline their collective efforts. This collaborative approach minimizes duplication of work and accelerates the process of discovery.
- Focus on Virus Behavior : A significant part of research coordination involves studying the transmission and mutation patterns of the mpox virus. By tracking how different variants behave, including the recently identified clade Ib, researchers can predict potential shifts in the outbreak’s trajectory and develop targeted responses.
- Encouraging Clinical Trials : WHO has also been instrumental in promoting clinical trials for potential vaccines and treatments. Regulatory pathways have been expedited to ensure that promising candidates can be tested efficiently without compromising safety. For example, several vaccine candidates have progressed through clinical trials, with early-stage results showing promise in stimulating effective immune responses.
- Data Collection and Sharing : To support these endeavors, WHO encourages countries to enhance data collection, enabling a better understanding of the global landscape of mpox infections. This focus on data not only helps monitor the outbreak but also informs vaccine development and deployment strategies.
By fostering an environment where researchers can work together seamlessly, WHO has positioned itself at the forefront of efforts to generate valuable insights that will ultimately lead to a more robust public health response.
Focus on Equitable Access
Equitable access to vaccines and treatments is a core principle guiding WHO’s strategies against mpox. The organization understands that simply developing effective vaccines is not enough; ensuring that these tools reach the populations that need them the most is equally crucial.
- Addressing Health Inequities : WHO’s proactive stance on equitable access is rooted in the recognition of disparities faced by different communities, especially in low- and middle-income countries. From the very onset of the mpox outbreak, WHO has worked diligently to ensure that marginalized and vulnerable populations receive prioritized access to vaccines, thereby mitigating the impact of the disease across varied demographics.
- Vaccine Sharing Initiatives : Through programs like COVAX, WHO has spearheaded initiatives to facilitate vaccine sharing globally. This mechanism aims to provide low-income countries with access to vaccines as they become available, ensuring that no nation is left behind during this health crisis. The intent is to create a unified approach toward vaccination that fosters global public health security.
- Community Engagement : An essential aspect of ensuring equitable access is engaging communities in the decision-making process. WHO emphasizes the importance of listening to the needs and concerns of affected populations. This approach helps tailor public health initiatives that resonate with communities, increasing the likelihood of vaccination uptake.
- Mental Health and Stigma Reduction : WHO also recognizes the role stigma can play in hindering access to medical resources. By integrating education and outreach into vaccination efforts, the organization aims to reduce fear and encourage individuals to seek care without hesitation.
In conclusion, the concerted research efforts and focus on equitable access led by WHO are crucial in the global response to mpox. By fostering collaboration among researchers and ensuring that vaccines and treatments reach all corners of the world, WHO is paving the way toward effective and meaningful public health results. As communities worldwide continue to face the challenges posed by mpox, these strategies will play an essential role in safeguarding health and well-being against the backdrop of an ongoing outbreak. Moving forward, the goal remains clear: to secure a healthier future for everyone through cooperative and inclusive efforts.
Global Health Systems Strengthening
As the mpox outbreak continues to unfold, the need for resilient and effective health systems has never been more critical. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes that a strong healthcare foundation is vital not only for managing current outbreaks but also for preparing for future public health challenges. In this context, WHO has emphasized collaborative efforts with member states and facilitated access to essential tools as key strategies for strengthening global health systems.
Collaborative Efforts with Member States
WHO has actively engaged with member states to reinforce their health infrastructure and better prepare for infectious disease threats like mpox. This collaboration is reflective of a shared commitment to enhancing public health systems worldwide.
- Tailored Support : Different countries face unique health challenges, and WHO has made it a priority to provide tailored support based on the specific needs of each member state. For instance, countries with limited healthcare resources received guidance on developing effective response frameworks that align with their existing capabilities.
- Training and Capacity Building : WHO has initiated training programs aimed at strengthening the skills of health professionals. These programs focus on surveillance, case management, and public health communications—critical areas that can make a significant difference during an outbreak. Personal anecdotes from healthcare workers reveal that these training sessions have empowered them to approach mpox cases with greater confidence and competence.
- Data Sharing and Communication : Effective communication and data sharing between WHO and member states have resulted in improved transparency regarding mpox statistics, outbreaks, and response effectiveness. By fostering a culture of communication, WHO ensures that countries can learn from one another’s experiences, building a collective knowledge base to tackle similar health challenges.
- Community Engagement : Realizing the importance of community in public health, WHO has stressed the need for member states to include community voices in decision-making processes. By identifying key community leaders and stakeholders, countries have developed initiatives that resonate with local populations, encouraging them to take part in prevention efforts.
These collaborative endeavors create a more robust health system infrastructure, equipping countries to deal not just with mpox but a myriad of public health challenges in the long term.
Facilitating Access to Tools
Facilitating access to essential health tools is a core component of WHO’s strategy to strengthen global health systems. The organization understands that the availability of vaccines, therapeutics, diagnostics, and other medical tools is critical in controlling outbreaks effectively.
- Global Vaccine Distribution : WHO has played a central role in ensuring that vaccines are distributed equitably across the world. Through initiatives such as COVAX, WHO aims to provide vaccines to low- and middle-income countries, which often face barriers in accessing crucial health resources. By working to eliminate disparities in vaccine availability, WHO strengthens the global health response to diseases like mpox.
- Availability of Diagnostics : The importance of reliable diagnostic tools cannot be understated. WHO has facilitated the development and distribution of testing kits, allowing countries to identify mpox cases swiftly. This rapid detection is vital for controlling outbreaks, as timely intervention helps prevent further transmission. Many health clinics have shared how access to reliable testing has radically improved their response times during outbreaks.
- Supporting Healthcare Infrastructure : In addition to just providing tools, WHO recognizes the need to bolster healthcare infrastructure. By supplying member states with the necessary funding, technical expertise, and materials, WHO helps countries establish and maintain effective health systems. This support includes enhancing laboratory capacities and ensuring that healthcare facilities are equipped to handle surges in patient care during outbreaks.
- Educational Resources and Training : WHO has also provided educational resources to both healthcare professionals and the general public. Informational campaigns addressing hygiene practices, vaccination importance, and stigma reduction have been instrumental in fostering acceptance and understanding of mpox within communities.
In summary, strengthening global health systems through collaborative efforts with member states and facilitating access to essential tools is imperative for tackling the mpox outbreak effectively. The alignment of local and global resources creates a framework where countries can respond to public health threats more efficiently and compassionately. As we look to the future, it’s clear that these elements will play a crucial role in fostering resilient health systems that can adapt to whatever challenges may arise. Together, through cooperation and resource-sharing, we can navigate the complexities of public health and strive toward a healthier global community.
